DFS, BFS
DFS
시작 node부터 시작해서 자식 node마다 재귀적으로 경로를 검색하는 방식으로, 목적지 node에 도착할 때까지 반복합니다.
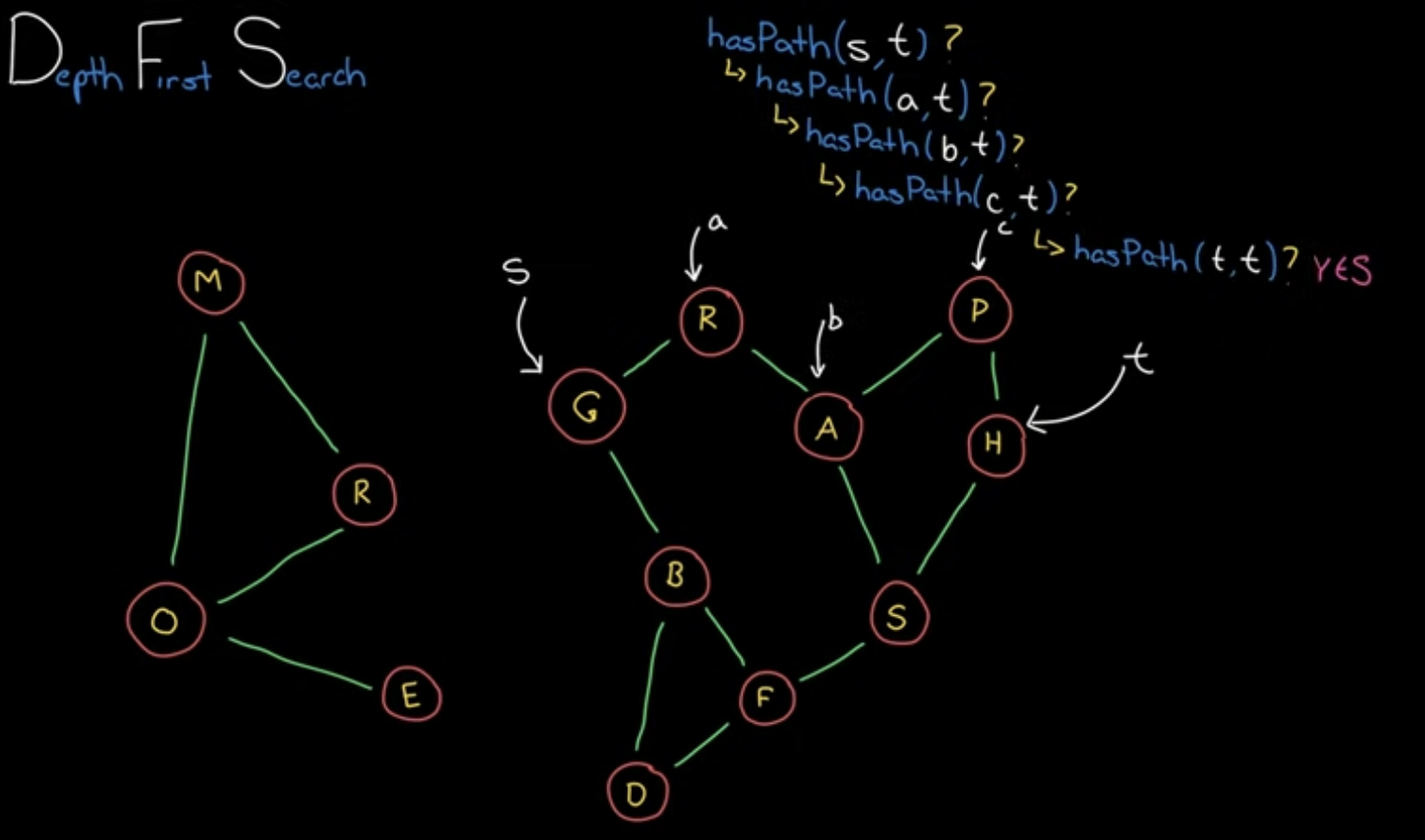
단거리로 갈 수 있음에도 불구하고 다른 경로를 택해서 우회하여 도착할 가능성이 다분하다는 단점이 있습니다.
보통 node X에서 node Y로의 경로 존재여부나 개수 등을 구할 때 자주 활용됩니다.
구현코드
js
// 정사각형 binary grid 형태로 제공된 그래프인 경우
const dfs = (adj) => {
const visited = new Set();
const hasPath = (src, dst) => {
if (visited.has(src)) {
return false;
}
if (src === dst) {
return true;
}
visited.add(src);
for (let next = src + 1; next < adj.length; next++) {
// 다음 재귀를 시작하기 위한 조건은?
if (adj[src][next] && hasPath(next, dst)) {
return true;
}
}
// 해당 케이스에 대한 탐색이 끝났으면 visited를 원래대로 돌려놓습니다.
visited.delete(src);
};
return {
hasPath,
};
};
WARNING
안타깝게도 위 방식은 양방향 그래프에서만 활용할 수 있습니다.
단방향에서 임의의 두 노드 간의 경로 존재여부는 Floyd-Warshall Algorithm을 사용하면 됩니다.
BFS
시작 node부터 시작해서 자식 node가 목적지 node인지 여부를 level을 넓혀가면서 탐색하는 방식입니다.
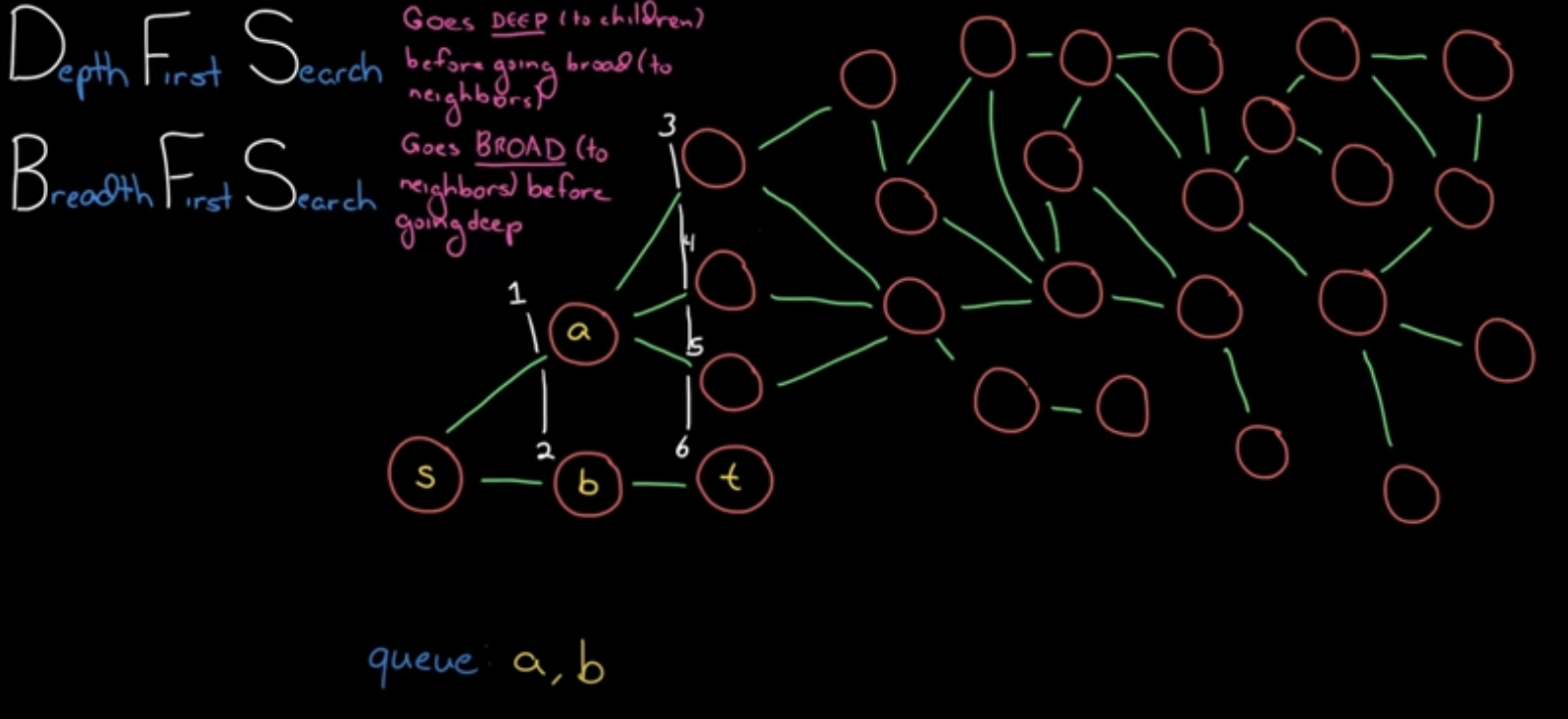
보통 queue로 구현하고, 특정 node로의 최단거리를 구할 때 자주 활용됩니다.
구현코드
js
const bfs = (adj) => {
const q = [];
const visited = new Set();
const hasPath = (src, dst) => {
q.push(src);
while (q.length) {
const x = q.shift();
// 이미 방문한 node라면 다음 node를 뽑습니다.
if (visited.has(x)) {
continue;
}
if (x === dst) {
return true;
}
visited.add(x);
for (let c = x + 1; c < adj.length; c++) {
// queue에 push하여 예약할 수 있는 조건은?
adj[x][c] && q.push(c);
}
}
return false;
};
return {
hasPath,
};
};
응용
- 미로에서 최소경로 구하기
js
const maps = [...] // 2차원 인접행렬로 주어진 미로
const [m, n] = [maps.length, maps[0].length];
const dx = [0, 1, 0, -1];
const dy = [1, 0, -1, 0];
const q = [[0, 0, 1]]; // q에 저장되는 지점 정보 : [x좌표, y좌표, 해당 지점까지 최단거리]
const visited = new Set();
while (q.length) {
const [px, py, dist] = q.shift();
const pStr = `${px}_${py}`;
if (visited.has(pStr)) {
continue;
}
if (px === m - 1 && py === n - 1) {
return dist;
}
visited.add(pStr);
for (let i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
const [nx, ny] = [px + dx[i], py + dy[i]];
if (nx < 0 || m <= nx || ny < 0 || n <= ny || !maps[nx][ny]) {
continue;
}
q.push([nx, ny, dist + 1]);
}
}
return -1;