Inside Fiber: an in-depth overview of the new reconciliation algorithm in React
Overview of the Sample Application
class ClickCounter extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = { count: 0 };
this.handleClick = this.handleClick.bind(this);
}
handleClick() {
this.setState((state) => {
return { count: state.count + 1 };
});
}
render() {
return [
<button key="1" onClick={this.handleClick}>
Update counter
</button>,
<span key="2">{this.state.count}</span>,
];
}
}
위 ClickCounter 컴포넌트에 "Update counter" 버튼을 클릭하면 아래와 같은 작업들이 필요합니다.
state.coutner의 값을 업데이트- 하위 React Element(이하 react-el)에 대해서 diff 계산
- Life Cycle 메서드 실행
- ref 업데이트
- ...
이와 같이 컴포넌트 렌더링 즉, 함수의 실행으로 처리해야 하는 일련의 작업들을 Fiber Architecure에서는 "work"라고 칭합니다.
work는 react-el의 type에 따라 달라지고 react-el은 컴포넌트의 render 메서드에서 반환됩니다.
From React Elements to Fiber nodes
React Elements
ClickCounter 컴포넌트에서 반환되는 배열은 Babel에 의해서 아래와 같이 변환되고
class ClickCounter {
...
render() {
return [
React.createElement(
'button',
{
key: '1',
onClick: this.onClick
},
'Update counter'
),
React.createElement(
'span',
{
key: '2'
},
this.state.count
)
]
}
}
React.createElement 메서드로 아래와 같은 객체가 생성됩니다.
[
{
$$typeof: Symbol(react.element),
type: 'button',
key: "1",
props: {
children: 'Update counter',
onClick: () => { ... }
},
// ...
},
{
$$typeof: Symbol(react.element),
type: 'span',
key: "2",
props: {
children: 0
},
// ...
}
]
ClickCounter 컴포넌트가 상위 컴포넌트에서 사용되면 아래와 같은 react-el로 변환됩니다.
{
$$typeof: Symbol(react.element),
key: null,
props: {},
ref: null,
type: ClickCounter
}
Fiber nodes
컴포넌트 최초 렌더링 중에 react-el은 각자 대응되는 Fiber Node(이하 fiber)를 가지는데 react-el과 다르게 리렌더링마다 새로 생성(=immutable)되지 않고 heap 메모리에 저장되는 객체로 컴포넌트의 state와 DOM, 그리고 수행할 work에 관한 정보를 가집니다.
여기서 fiber는 처리할 work에 따라 다른 타입인 workTag를 가지고 React는 fiber 단위로 scheduling을 구현합니다.
fiber는 react-el의 속성들을 인자로 받는 createFiberFromTypeAndProps 함수로부터 생성됩니다.
이후 update가 발생할 때마다 React는 react-el에 대응되는 fiber에 접근하여 직접 필요한 속성을 수정(=mutable)하거나 react-el의 key props를 기준으로 위치가 옮기거나 render 메서드로부터 반환되지 않을 시 제거합니다.
fiber가 수행하는 work들은 ChildReconciler 함수에서 확인할 수 있습니다.
fiber들은 react-el의 관계에 맞춰서 child, sibling, return 속성으로 참조하는 방식으로 연결되어 있습니다.
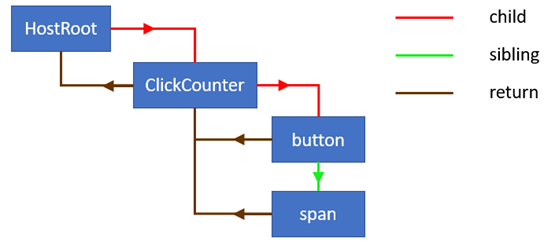
Current and work in progress trees
임의의 컴포넌트를 처음으로 렌더링하고 나서 현재 UI의 state를 반영한 fiber tree가 생성되는데 이를 "curent tree"라고 칭합니다.
이후 React에서 update들을 처리하면서 추후 화면에 반영될 state를 지닌 "workInProgress tree"도 만들어집니다.
React는 리렌더링이 일어나면 current tree의 root에서 내려오면서 render 메서드로 반환된 react-el의 정보를 담은 workInProgress node(=fiber)를 생성하고 여기에 정의된 work를 처리합니다.
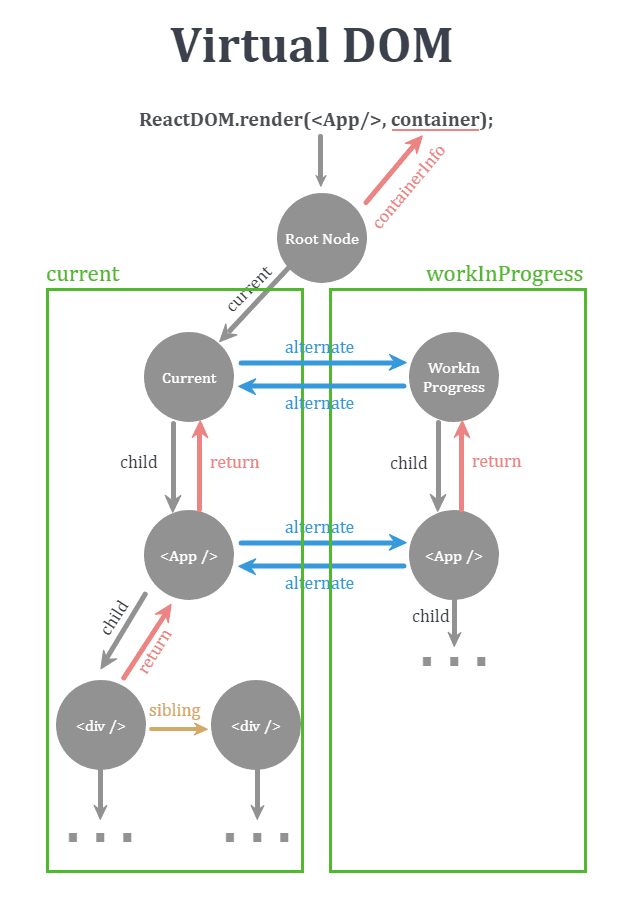
workInProgess tree에서 모든 work들이 처리되면 해당 tree가 current tree가 되고 commit phase로 넘어가서 화면에 그려집니다(=flush).
실제 소스를 확인하면 current node와 workInProgress node를 인자로 받는 work가 여러 개 정의되어 있는데, 여기서 두 node는 서로 alternate 속성으로 참조하는 관계를 가집니다.
function updateHostComponent(current, workInProgress, renderExpirationTime) {
// ...
}
Side-effects
React에서 컴포넌트가 state, props를 기반으로 UI를 계산하는 함수라면 Effect는 commit phase에 수행되는 DOM manipulation, Life Cycle 메서드 호출, useEffect hook으로 정의된 작업 등을 가리킵니다.
🤔 DOM manipulation effect는 reconciliation 과정을 통해서 지정되는 것으로 추측할 수 있습니다.
fiber는 effect도 work로 간주하므로 react-el에서 처리되는 effect의 종류에 맞는 effectTag를 가집니다.
Effects list
React는 effect가 있는 fiber들을 linked list로 연결하여 iterate하는 방식으로 effect를 빠르게 처리합니다.
effects list를 구성하는 fiber는 nextEffect 속성으로 다음에 처리할 fiber를 참조하고 hostRoot의 firstEffect는 처음으로 처리할 effect를 가진 fiber를 참조합니다.
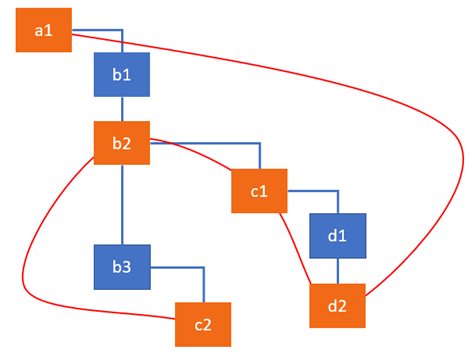
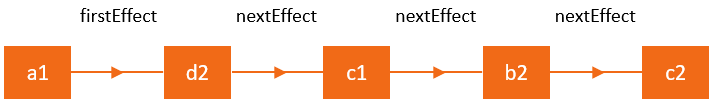
Root of the fiber tree
React app은 <div id="root" />와 같이 container 역할을 하는 node가 적어도 하나씩 있습니다.
const domContainer = document.querySelector("#root");
ReactDOM.render(React.createElement(ClickCounter), domContainer);
이러한 container에 대해서 "fiber root"라는 객체를 생성하는데 이는 DOM을 통해서 접근할 수 있습니다.
const fiberRoot = query("#container")._reactRootContainer._internalRoot;
그리고 React는 fiber root를 통해서 실제 fiber tree(current tree)의 root인 "host root"를 참조할 수 있습니다.
const hostRootFiberNode = fiberRoot.current;
host root는 "HostRoot"라는 특수한 타입을 가진 fiber이고 stateNode 속성을 통해 fiber root를 참조할 수 있습니다.
hostRootFiberNode.stateNode === fiberRoot; // true
컴포넌트에 대응되는 fiber는 아래와 같이 참조할 수 있습니다.
compInstance._reactInternalFiber;
추가적으로 current tree의 root와 workInProgress tree의 root는 서로 alternate 속성으로 참조하고 있습니다.
Fiber node structure
위 예시에서 등장한 ClickCounter 컴포넌트와 span react-el로부터 생성되는 fiber는 각각 다음과 같은 구조를 가집니다.
{
stateNode: new ClickCounter,
type: ClickCounter,
alternate: null,
key: null,
updateQueue: null,
memoizedState: {count: 0},
pendingProps: {},
memoizedProps: {},
tag: 1,
effectTag: 0,
nextEffect: null
}
{
stateNode: new HTMLSpanElement,
type: "span",
alternate: null,
key: "2",
updateQueue: null,
memoizedState: null,
pendingProps: {children: 0},
memoizedProps: {children: 0},
tag: 5,
effectTag: 0,
nextEffect: null
}
fiber를 구성하는 속성들을 일부를 정리하면 아래와 같습니다.
stateNode- fiber와 연관된 react-el를 참조하고 fiber가 관리하는 local state를 들고 있습니다.
type- fiber와 연관된 react-el의 종류(class constructor, 함수, HTML tag 이름)를 의미합니다.
tag- fiber가 처리하는 work의 종류를 가리키는 workTag입니다.
- 위 예시에서
tag: 1은 "ClassComponent",tag: 5는 "HostComponent"를 의미합니다.
updateQueue- batch로 처리할 state update들이 queue 구조로 저장됩니다.
memoizedState- 현재 화면에 그려진 output을 반영한 state입니다.
memoizedProps- 현재 화면을 렌더링할 때 적용된 props입니다.
pendingProps- 리렌더링에 의해서 적용할 새로운 props입니다.
key- 배열 구조로 나열된 react-el들을 구분하기 위한 고유한 id입니다.
- 리렌더링 전후로 어떤 item이 추가되거나 삭제되었는지, 또는 어떻게 순서가 바뀌었는지를 계산할 때 사용합니다.
General algorithm
React는 두 단계에 걸쳐서 work를 처리합니다.
첫번째 render 단계에서 setState나 React.render의 호출에 의해 update 작업이 수행되고 현재 UI에 필요한 변경사항을 계산합니다.
최초 렌더링이라면 React는 개별 react-el에 대응되는 fiber를 생성하고 이후 update가 적용될 때마다 기존의 fiber를 재사용하거나 직접 수정합니다(어디서 언급된건지🤔).
그리고 render 단계를 진행하면서 두번째 commit 단계에서 수행할 effect를 개별 fiber에 지정하고 effect를 지닌 fiber들은 linked-list 구조로 연결되어 commit 단계에서 순서대로 처리됩니다.
render 단계에서 work들은 가용시간 동안 1개 이상 처리되는 중에 임의의 사용자 이벤트 같이 급한 task가 생기면 stash되고 나서 중지된 지점으로부터 work를 재개할 수 있는 즉, 비동기적으로 처리됩니다.
이 과정에서 일부 work들이 폐기되어 다른 work가 시작되거나 top root로부터 시작하는 경우도 일어납니다.
반면 phase 단계에서 수행하는 work들은 화면에 바로 반영되기 때문에 중간에 멈추지 않고 동기적으로 처리됩니다.
추가적으로 render 단계와 commit 단계에서 수행되는 클래스 컴포넌트의 Life Cycle 메서드가 아래와 구분됩니다.
render
UNSAFE_componentWillMount(deprecated)UNSAFE_componentWillReceiveProps(deprecated)getDerivedStateFromPropsshouldComponentUpdateUNSAFE_componentWillUpdate(deprecated)render
commit
getSnapshotBeforeUpdatecomponentDidMountcomponentDidUpdatecomponentWillUnmount
위에서 UNSAFE_ prefix가 붙은 메서드들은 개발자들이 용도를 오해해서 commit 단계에 수행할 effect들을 지정하는 실수를 방지하고자 붙여졌습니다.
이제 각 단계별로 실행되는 코드를 살펴보겠습니다.
Render phase
render 단계는 renderRoot 함수를 사용하여 hostRoot에서 시작됩니다.
여기서 React는 실제로 render를 trigger한 fiber를 찾을 때까지 이미 work가 처리된 fiber들을 skip하여 불필요한 연산이 없도록 합니다.
child, sibling, return 등의 속성으로 연결된 fiber들은 work loop를 통해 재귀적으로 처리됩니다.
function workLoop(isYieldy) {
if (!isYieldy) {
while (nextUnitOfWork !== null) {
nextUnitOfWork = performUnitOfWork(nextUnitOfWork);
}
} else {...}
}
nextUnitOfWork는 상에서 처리할 work가 있는 다음 workInProgress node(=fiber)를 참조하는 변수로, 값이 null이 될 때까지 while 루프를 돌다가 이 루프에서 벗어나면 commit 단계가 시작됩니다.
work loop 내에서 work를 처리하는 4개의 주요 함수가 있는데 동작방식은 아래 이미지로 확인할 수 있습니다.
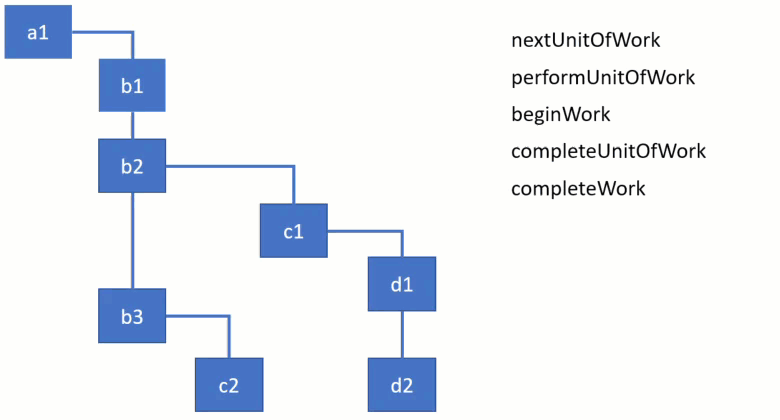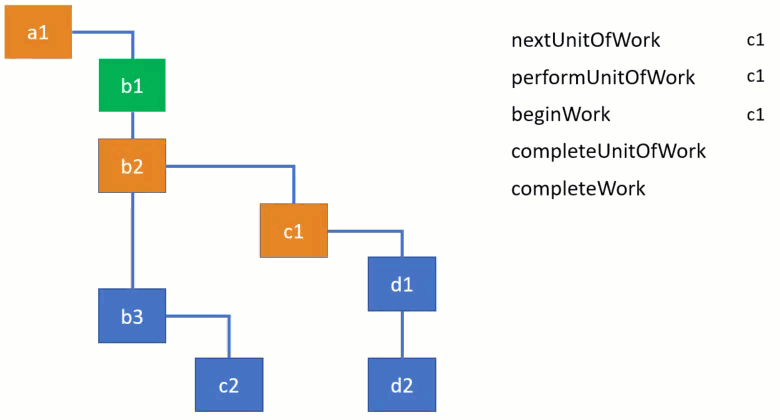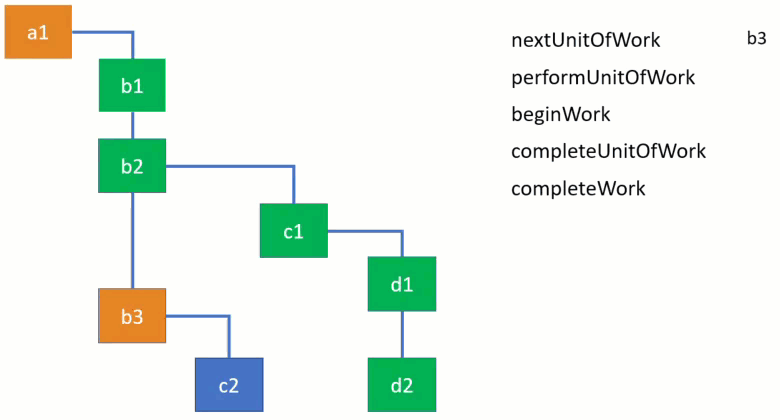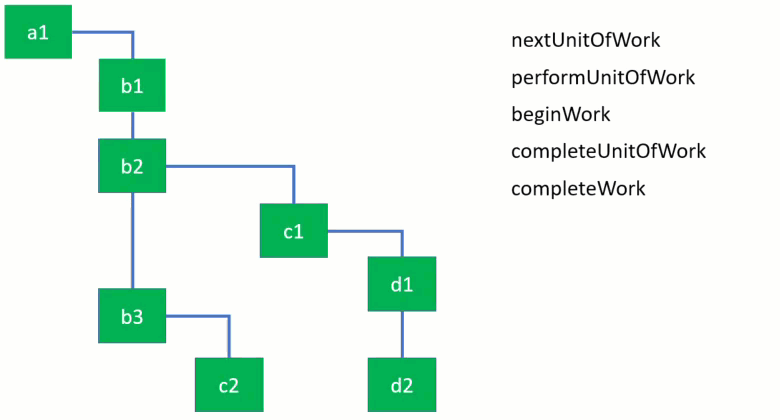
performUnitOfWork 함수는 beginWork 함수가 지정한 workInProgress node의 work를 처리하는데 여기서 beginWork 함수는 현재 위치한 node의 child node를 반환합니다.
function performUnitOfWork(workInProgress) {
let next = beginWork(workInProgress);
if (next === null) {
next = completeUnitOfWork(workInProgress);
}
return next;
}
function beginWork(workInProgress) {
console.log("work performed for " + workInProgress.name);
return workInProgress.child;
}
work loop를 통해 child node들을 처리하다가 leaf node에 도착하면 completeUnitOfWork 함수를 실행하여 현재 node의 sibling node들을 처리하고 나서 다시 parent node로 돌아갑니다(=backtrack).
function completeUnitOfWork(workInProgress) {
while (true) {
let returnFiber = workInProgress.return;
let siblingFiber = workInProgress.sibling;
nextUnitOfWork = completeWork(workInProgress);
if (siblingFiber !== null) {
// If there is a sibling, return it
// to perform work for this sibling
return siblingFiber;
} else if (returnFiber !== null) {
// If there's no more work in this returnFiber,
// continue the loop to complete the parent.
workInProgress = returnFiber;
continue;
} else {
// We've reached the root.
return null;
}
}
}
function completeWork(workInProgress) {
console.log("work completed for " + workInProgress.name);
return null;
}
Commit phase
commit phase는 completeRoot 함수를 사용하여 hostRoot에서 시작됩니다.
이 단계에 도달했을 때 현재 화면에 그려진 state를 반영한 current tree와 render 단계를 거치면서 생성된 workInProgress(또는 finishedWork) tree가 있습니다.
뿐만 아니라 render 단계를 거치면서 commit 단계에 실행할 effect가 지정된 finishedWork tree의 일부 node들은 nextEffect 속성으로 연결되어 effects list를 구성합니다.
실제 commit 단계에서 동작하는 주된 함수는 commitRoot로 아래와 같은 작업들을 순서대로 처리합니다.
getSnapshotBeforeUpdatea.SnapShoteffectTag를 지닌 fiber에 한해서 실행되는 Life Cycle 메서드입니다.componentWillUnmounta.DeletioneffectTag를 지닌 fiber에 한해서 실행되는 Life Cycle 메서드입니다.모든 DOM insertion, update, deletion 작업
finishedWork tree를 current tree로 지정
componentDidMounta.PlacementeffectTag를 지닌 fiber에 한해서 실행되는 Life Cycle 메서드입니다.componentDidUpdatea.UpdateeffectTag를 지닌 fiber에 한해서 실행되는 Life Cycle 메서드입니다.
- ...
여기서 4번 기준으로 이전 작업들은 current tree를 참조하고, 이후 작업들은 workInProgress tree를 참조한다는 점에서 구분할 수 있습니다.
위에서 나열한 작업들은 다음과 같이 개별 함수로 정의됩니다.
function commitRoot(root, finishedWork) {
// pre-mutation
commitBeforeMutationLifecycles();
// All DOM manipulation
commitAllHostEffects();
root.current = finishedWork;
// post-mutation
commitAllLifeCycles();
}
개별 함수는 finishedWork tree의 effects list를 순회하면서 함수의 목적에 부합하는 effectTag를 가진 fiber들을 대상으로 work를 처리합니다.
commitAllHostEffects 함수에서 수행하는 DOM manipulation은 여기서 확인할 수 있습니다.