Map
reference 타입 중 하나인 Map은 key-value pair로 속성을 저장한다는 점에서 일반적인 객체와 거의 비슷하지만 다음과 같은 차이점이 있습니다.
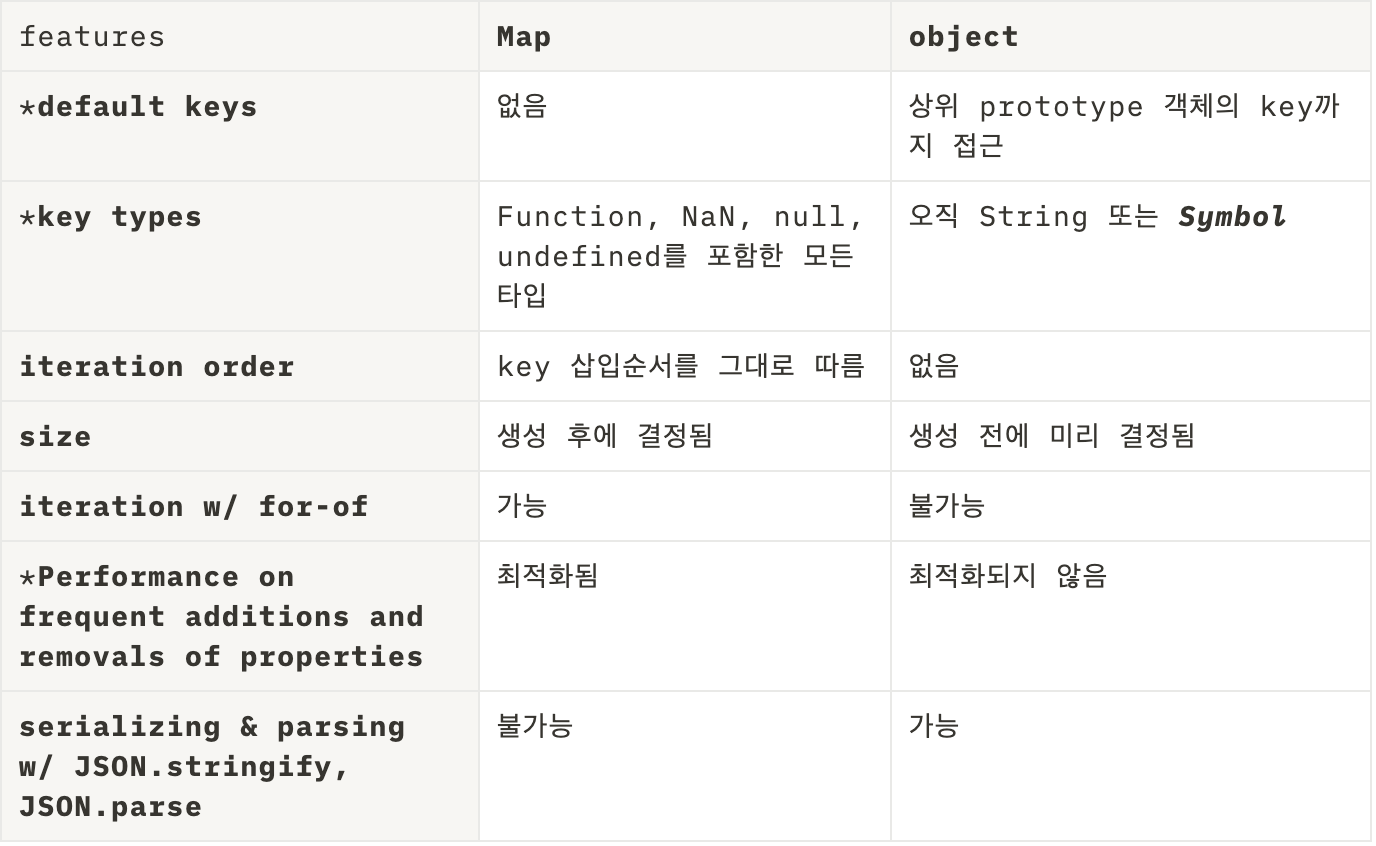
Map과 Object의 차이점
Iterating Map with forEach method
js
myMap.forEach((value, key) => {
console.log(key + " = " + value);
});
// 0 = zero
// 1 = one
2D Array
js
const kvArray = [
["key1", "value1"],
["key2", "value2"],
];
// Use the regular Map constructor to transform a 2D key-value Array into a map
const myMap = new Map(kvArray);
myMap.get("key1"); // returns "value1"
// Use Array.from() to transform a map into a 2D key-value Array
console.log(Array.from(myMap));
// A succinct way to do the same, using the spread syntax
console.log([...myMap]);
// Or use the keys() or values() iterators, and convert them to an array
console.log(Array.from(myMap.keys())); // ["key1", "key2"]
Cloning Maps
js
const original = new Map([[1, "one"]]);
const clone = new Map(original);
console.log(clone.get(1)); // one
console.log(original === clone); // false (useful for shallow comparison)
Merging Maps
js
const first = new Map([
[1, "one"],
[2, "two"],
[3, "three"],
]);
const second = new Map([
[1, "uno"],
[2, "dos"],
]);
// Merge two maps. The last repeated key wins.
// Spread operator essentially converts a Map to an Array
const merged = new Map([...first, ...second]);
console.log(merged.get(1)); // uno
console.log(merged.get(2)); // dos
console.log(merged.get(3)); // three